Text
- Headings
HTML defines six levels of headings. A heading element implies all the font changes, paragraph breaks before and after, and any white space necessary to render the heading. The heading elements are H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, and H6 with H1 being the highest (or most important) level and H6 the least.


- Paragraphs
The <p> HTML element represents a paragraph. Paragraphs are usually represented in visual media as blocks of text separated from adjacent blocks by blank lines and/or first-line indentation, but HTML paragraphs can be any structural grouping of related content, such as images or form fields.
- Bold
<b>
By including words in the tags <b> and </b> we can make characters appear bold.

- Italic
By including words in the tags <i> and </i> we can make characters appear italic


- Superscript & Subscrip
The <sup> element is used to contain characters that should be superscript such as the suffixes of dates or mathematical concepts like raising a number to a power such as 22
<sup> text </sup>
**The element is used to contain characters that should be subscript. It is commonly used with foot notes or chemical formulas such as H20**
<sub>text</sub>
- Line Breaks
<br />
- Horizontal Rules
<hr />
Summary
-
HTML elements are used to describe the structure of the page (e.g. headings, subheadings, paragraphs).
-
They also provide semantic information (e.g. where emphasis should be placed, the definition of any acronyms used, when given text is a quotation).
Introducing CSS
What is CSS?
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets with an emphasis placed on “Style.” While HTML is used to structure a web document (defining things like headlines and paragraphs, and allowing you to embed images, video, and other media), CSS comes through and specifies your document’s style—page layouts, colors, and fonts are all determined with CSS.
How Does CSS Work?
CSS brings style to your web pages by interacting with HTML elements. Elements are the individual HTML components of a web page—for instance a paragraph—which in HTML might look like this:
<p>This is my paragraph!</p>
If you wanted to make this paragraph appear pink and bold to people viewing your web page through a web browser, you’d use CSS code that looks like this:
p { color:pink; font-weight:bold; }
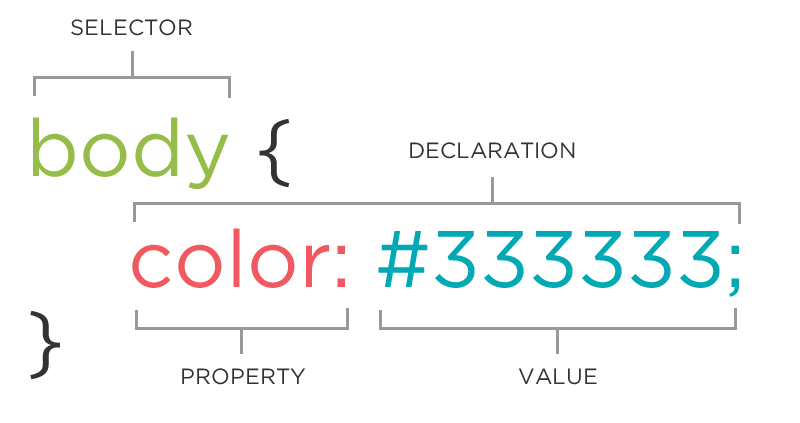
selector and a declaration
CSS Associates Style rules with HTML elements
CSS works by associating rules with HTML elements. These rules govern how the content of specified elements should be displayed. A CSS rule contains two parts: a selector and a declaration.
a property and a value
CSS Properties Affect How Elements Are Displayed
CSS declarations sit inside curly brackets and each is made up of two parts: a property and a value, separated by a colon. You can specify several properties in one declaration, each separated by a semi-colon.
Summary
-
CSS treats each HTML element as if it appears inside its own box and uses rules to indicate how that element should look.
-
Rules are made up of selectors (that specify the elements the rule applies to) and declarations (that indicate what these elements should look like).
-
Different types of selectors allow you to target your rules at different elements.
Basic JavaScript instructions
- Statements:
A script is a series of instructions that a computer can follow one-by-one. Each individual instruction or step is known as a statement. Statements should end with a semicolon.
- Comments:
You should write comments to explain what your code does. They help make your code easier to read and understand. This can help you and others who read your code
/* commits */
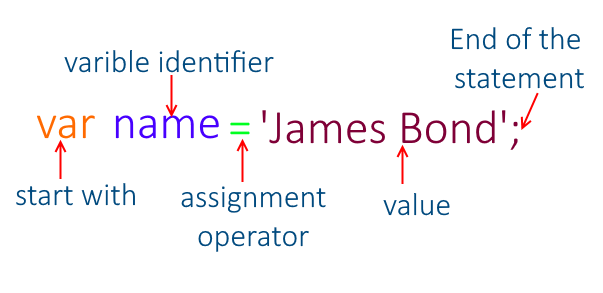
- WHAT IS A VARIABLE?
Variable means anything that can vary. In JavaScript, a variable stores the data value that can be changed later on. Use the reserved keyword var to declare a variable in JavaScript.
Summary
-
A script is made up of a series of statements. Each statement is like a step in a recipe.
-
Scripts contain very precise instructions. For example, you might specify that a value must be remembered before creating a calculation using that value.
-
Variables are used to temporarily store pieces of information used in the script.
Decisions
- Decision Making in programming is similar to decision making in real life.
- A programming language uses control statements to control the flow of execution of the program based on certain conditions.
- JavaScript’s conditional statements are: 1) if 2) if-else 3) if…else…if 4) switch
Looping Statements
- Looping in programming languages facilitates the execution of a set of instructions/functions repeatedly while some condition evaluates to true.
- For example, suppose we want to print “Hello World” 10 times this is possible with the help of loops.
-
There are mainly two types of loops: 1) Entry Controlled loops: In this type of loops the test condition is tested before entering the loop body. For Loop and While Loop are entry controlled loops. 2) Exit Controlled Loops: In this type of loops the test condition is tested or evaluated at the end of loop body. Therefore, the loop body will execute atleast once, irrespective of whether the test condition is true or false. do-while loop is exit controlled loop.
- Following are the types of loops in JavaScript: 1) while loop 2) do-while loop 3) for loop 4) for…in loop